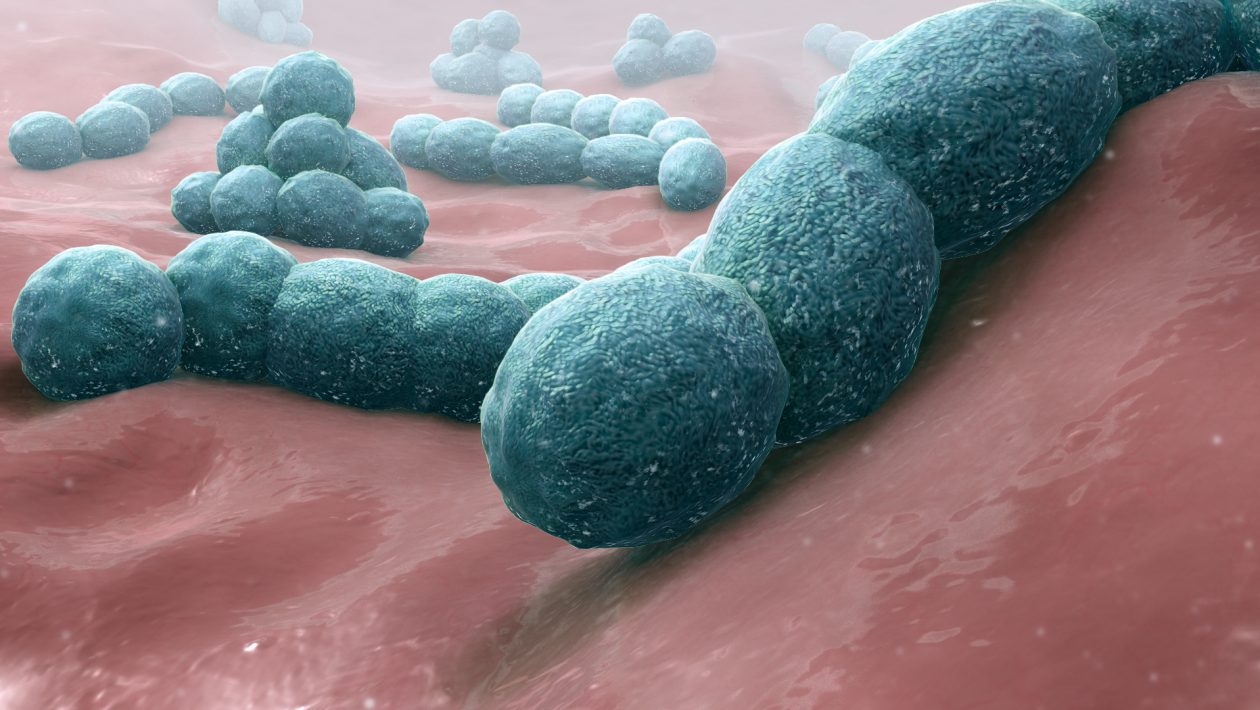
Most of the serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae are disease-causing, but only a minor section of this bacterial population is the reason for major pneumococcal infections. These bacteria are the reason for the maximum cases of pneumonia that is acquired from the community.
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive bacterium that is pathogenic and colonizes all the mucosal surfaces of the nasopharynx and upper airways of the host.
It can undergo virulent actions to weaken the immune responses of the host. Post this; the bacteria spread profusely from the upper respiratory tract to the lower regions.
Streptococcus pneumoniae shape is slightly shaped like a coccus, which is a bit pointed and non-motile. These bacteria do not form spores, and they usually live in chains that may vary in length. They are characteristically shaped round or ovoid structures.
Table of Contents
Characteristics of Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae are characteristically found to occur in pairs known as diplococci, but at times they also exist in the form of short chains and even remain single. These bacteria are non-motile organisms.
If you want to know, where is streptococcus pneumoniae found, then you should know, most of the people (around 5% to 90% of the healthy people) carry them in their noses. Upper respiratory tract especially the nasopharynx, throat in general, and skin, are the common places in the human body where you will find the bacteria.
Among the school children, 20% to 60% of them seem to be carriers; similarly, in a military installation, there can be 50–60% of them who are carriers of these bacteria.
However, it is also found that the duration of carriage is more extended in children compared to that of the adults.
These bacteria tend to get transferred to other parts of the body very easily through saliva and droplets of mucus. In most cases, they do not cause any illness, but they can also get transferred from one body to another through sneezes, sharing stuff, and coughs.
Symptoms
Streptococcus pneumoniae symptoms depend on the part of the body; it has attacked. As a result of the invasion, the infection may lead to severe chills, irritability, and high fever.
Patients give an anxious and grayish appearance and seem ill. Apart from these, occasional headaches, sleepiness, poor feeding, stiff neck, vomiting, and confusion in case the infection leads to meningitis.
In elderly patients, the respiratory rates elevate, but the body temperature does not necessarily increase; instead, it shows a slight elevation.
There can be sudden onsets of shaky chills, which may follow coughs. But rusty sputum has been classified as the distinct symptom of pneumococcal pneumonia even though it is pretty rare.
However, the symptoms do not appear on the body just immediately after the bacteria invade a body. There is an incubation period for 1 to 3 days, after which the symptoms are visible on the body the exposure. At certain sever or fatal conditions, the incubation period is longer than this. Moreover, a person who has been affected earlier by these bacteria can also be attacked again.
Specifically, the symptoms vary and depend on the infection:
- If an infection develops in the sinuses, symptoms that may appear are headaches, teeth and face pain, nasal congestions, fever, and loss of smell, postnasal drips, and sore throat.
- For infection in the ear, symptoms of ear pain, trouble in sleeping, balance issues, and behavioral change are common. Babies or children get inconsolable and tug their ears.
- In the case of pinkeye, symptoms are like thick discharges that let the eyelids to stick when you sleep. The eyes turn watery, crusty, and red. You may feel gritty like sandpaper.
- Pneumonia develops symptoms of sudden high fevers, short breath, headache, and coughs with the production of mucus.
Diseases
The infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is a gram-positive, is the prime cause of community-acquired pneumonia and even endocarditis, peritonitis, sinusitis, osteomyelitis, and septic arthritis. These complications are diagnosed with procedural treatment methods.
Pneumococcal diseases are infections caused by the bacteria, Streptococcus pneumoniae and can lead to several illnesses, which may be like infections of the lungs or pneumonia, ear, and sinus infections.
These bacteria are also the chief reason for the occurrence of the disease, streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis (an infection around the covering of the spinal cord and the brain), and bacteremia (infection in the bloodstream).
Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria spread from an infected person to another through coughs, sneezes, and even through interpersonal contacts.
Causes of Streptococcus pneumonia infection
The chief cause of pneumococcal diseases in humans is that the bacteria are borne by people in their noses and throat even without sickness.
At times, the bacteria can affect your lungs, causing pneumonia and ears, causing otitis media. It is then considered as invasive if it’s found to enter the bloodstream of the patient and even the spinal fluids causing meningitis.
The streptococcus pneumoniae transmission occurs as the bacteria are spread from one person to another through direct exposure or by inhaling the air that contains the bacteria. It may reach a healthy body through an infected person’s sneezes or coughs.
Who are at risk of getting it?
There are many cases when a person can be at risk of being invaded by pneumococcal diseases. Among the adults, the cases may be:
- Anatomic and functional asplenia
- Smoking cigarettes
- With a decreased level of immune functions because of diseases and medications
- For leakage of cerebrospinal fluid and cochlear implants
- Chronic diseases of the heart, lungs (asthma), and even renal diseases
If children suffer from sickle-cell disease, hence the symptoms of anatomic and functional asplenia appear in them. Some children get affected by the bacteria due to prior HIV infections. These children are at higher risk of getting invaded by pneumococcal diseases.
Studies have also revealed that there are 50% more chances of bacteria invading bodies of children with these conditions rather than healthier ones.
Children from Africa, Alaska, and American Indians have more risk factors to worry about. Researchers have proved that attendance in child care centers also increases the risk by 2 to 4 folds of getting infected by these bacteria. This is specifically for younger children below the age of 59 months.
Apart from children, elderly people above the age of 65 years also form a part of the risked group. Thus, it is clear that people with weakened immunity are susceptible to invasions by S. pneumoniae.
Pneumococcal diseases affect people around the world, but the winter months, as well as early spring, are the most common periods when these bacteria are more viable in the tropics.
That is why; travelers are at the highest risk of suffering from pneumococcal diseases. They are the ones to spend most of the time in close contact with different people in such countries where the Streptococcus pneumoniae vaccine is not periodically provided to children.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis for Streptococcus pneumonia is dependent on the type of sickness but mostly, they are given antibiotics.
Patients of pneumonia are treated with quinoline, macrolide, amoxicillin, and doxycycline. In infectious diseases, there is no perfect treatment; the physicians need to make microbiologic means for the correct diagnosis.
The primary antibiotic theory is applied to keep the patient in check. These antibiotics are effective for treating mycoplasma for Chlamydophila.
There is a difference in the recommended drug in Sweden, where the patients are usually given penicillin. These are primarily for the patients whose treatment for pneumonia has not begun.
For infection in the middle ear or for sinusitis, bacterial cultivation is done to identify the causative agent for the infection. This process is time-draining, and hence an alternative technique has been adopted that is way quicker than this traditional method.
The alternative method takes 20 minutes that uses a liquid sample to diagnose the disease and it also identifies the causative bacterium. In the case of pneumonia coughed-up sputum, urine samples or nasal cavity swabs are tested for the diagnosis.
Treatment
Streptococcus pneumoniae causes invasive infections and are usually treated with antibiotics. The biggest concern is regarding the fact that these bacteria are increasingly becoming drug-resistant, which is resulting in overall misuses of antibiotic treatments.
This transformation is a natural phenomenon due to which the genetic material has undergone drastic shifts, and the exchange usually takes place between two organisms too.
The reasons are many for this change which may be mutation and natural selection. The natural transformation has also resulted in faster growth of the organisms and more antibiotic-resistant. Even the bacteria have made certain natural changes in their attributes; Erythromycin still works well for the infections caused by these bacteria.
Vaccines for the prevention of infections
There are many streptococcus pneumoniae treatment options for the infections of S. pneumoniae which are as follows:
First Aid
In milder cases, the doctors give penicillin V to the patients.
For severe infections, penicillin G is given. It is also given to patients with hypersensitivity to penicillin, but such vaccines are infused with erythromycin too.
Immunization
Vaccines are almost ineffective for children below the age of 2 years. Polyvalent vaccines that contain capsular polysaccharides are used for patients who are highly risked with a fatal infection. In that case, adults are given these vaccines so that there is no chance of systemic reactions.
At present, treatment methods usually include preventive steps. This is possible by using vaccines like 23-valent capsular polysaccharide. These vaccines will protect an individual from the common strains of the bacteria.
However, Streptococcus pneumoniae has different strains, which are about 90 in number. As a result, any vaccine that can counter all the strains is not developed yet.
Prevent invasion and spread of Streptococcus pneumoniae
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines are a must and need to be given to children following a basic routine. This helps to prevent the invasion of the bacteria, Streptococcus pneumoniae. Moreover, such countries where the vaccines are regularly given, there are fewer chances of outbreaks too.
In case you are a traveler, the streptococcus pneumoniae vaccine needs to be taken immediately before you begin your journey.
There are preventive steps that you need to follow. These are as follows:
- Adults above the age of 65 years need to take the PPSV23 or 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine.
- For the children above the age of 6 till 18 years and adults above the age of 19 years are also recommended to have doses of PCV13.
- Children till the age of 5 years should routinely receive about 4 doses of the different vaccines for pneumonia (PCV13 or 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine).
- So, you should make sure that your children receive all the doses of PCV13.
- Young adults who have a medical condition to worry about, and also smokers should get doses of PPSV23.
For preventing streptococcus pneumoniae pathogenesis in your body, practicing cleanliness and maintaining hygiene are the foremost requirements. You can do this by:
- Washing hands quite often, if you find soap and water not available, you can still clean your hands with sanitizers that have 60% alcohol content.
- While coughing or sneezing, cover your mouth and nose with a tissue and if a tissue is not available, at least use your sleeve and not your hands.
- Avoid touching your face, necks, eyes or ears more often. If you have to touch your face, do that after cleaning your hands.
- Avoid interpersonal contacts through hugging, sharing utensils with sick people.
Final thoughts
If at times you feel sick and chances are like you are suffering from pneumococcal disease, then talk to a doctor or nurse. But as it is usually said, prevention is better than cure.
Therefore vaccination is the best alternative. With the increasing number of resistant strains of Streptococcus, vaccine approaches are changed to look for antigens that are readily effective for a varied range of bacterial strains.