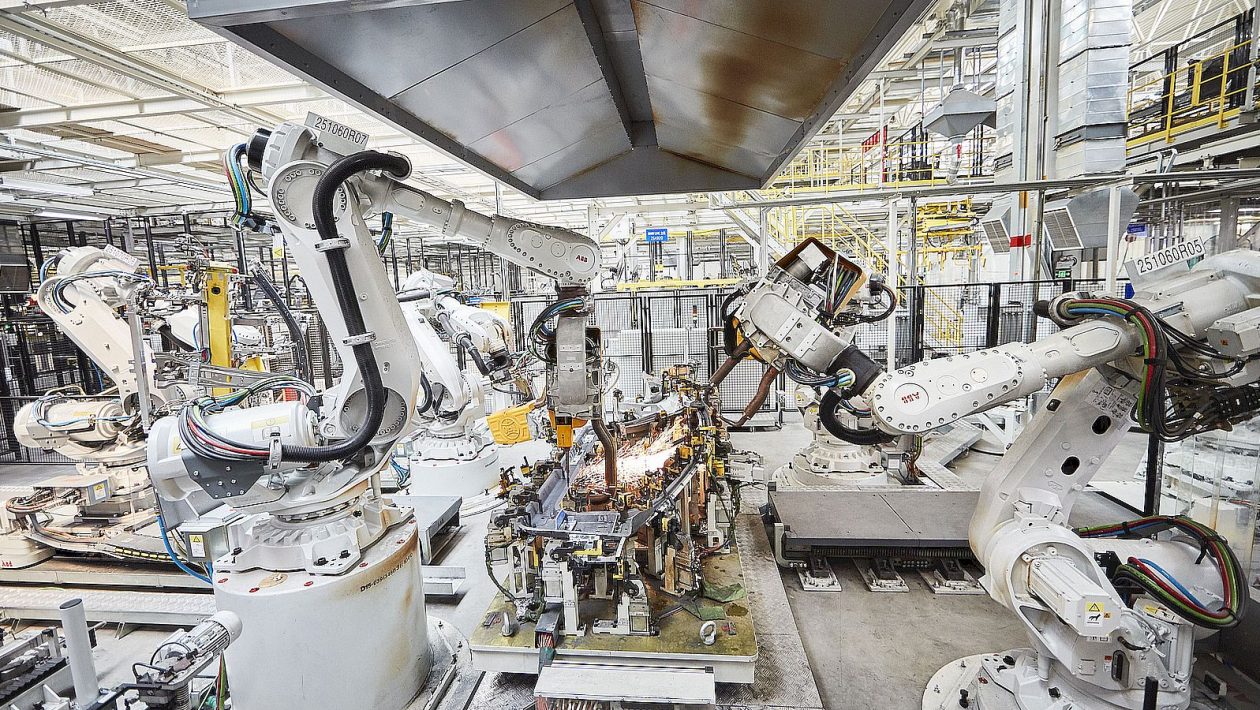
Unlike industrial robots used in the automotive sector as well as other machinery industries, we aim to focus on high complexity and low volume machines. These are the few robotic machines that are not only produced but also deployed within each specification. There are two realities that characterize the high complexity nature of industrial robots, they are:
- The first reality is that the breadth of different machine types that can be included in this category is massive.
- The second reality is that there is also a great variety when it comes to the technology and size of the robots as well as the application areas for these machines.
What are industrial robots?
Industrial robots are best defined according to the following:
- Their interaction with humans.
- Their physical attributes such as weight and reach among others.
- Their level of autonomy.
- Their mobility.
- Cobots – With over 10,000 to 20,000 units shipped in 2017, cobots are a rapidly growing market expected to increase by over 100,000 units by the end of 2020. Unlike stand-alone robots, collaborative robots do not require safety fences to operate safely. This is because they are designed with safety mechanisms allowing them to operate safely and directly alongside humans. With these in-built safety mechanisms, cobots do not need external safety measures such as interlock and fencing which in turn reduces the costs of installation design.
Cobots can also be easier to apply, connect and also run. Most of them consist of single robot installations comprising of discrete and simple input and output interfaces which lower both the cost of installations and programming. Anywhere workers stand to gain from physical support, these industrial robots for sale provide an advantage. For instance, they improve ergonomic processes by giving human stuff the assistance they need to be productive and succeed in manufacturing.
Collaborative robots are mostly deployed in electronic and automotive sectors where they are mostly used for incidental work which includes material handling. They are also used in value-adding processes such as assembly. Cobots are also used in supportive work such as pre-retail and kitting services as well as value-added tasks such as picking.
- Stand-alone industrial robots – According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), the estimated number of stand-alone industrial robots installed in 2017 worldwide was 2.1 million with a shipment of 381,000 units. Among these, handling operations such as assembly comprised of 47,000 units, soldering, and welding comprised of 82,000 units and machine tending 178,000 units.
The automotive industry was the largest market with 126,000 units followed by the electrical and electronics sector with 121,000 units.
The largest and reigning market was in Asia spearheaded by China, the biggest regional market with 138,000 units. 70% of the market was made up of five of the following countries.
- China
- South Korea
- Japan
- Germany
- United States
At 65%, the majority of shipments for industrial robots consisted of articulated arms in 2017.
Unlike cobots, stand-alone robots require the presence of safety equipment such as fences equipped with gates that are interlocked to the system for purposes of safety. Additionally, these machines operate exclusively without direct contact with the human staff. Usually, they are stationary and programmed to perform a specific task.
- Mobile robots – These are also known as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) meaning they can be used in a wide range of applications, including the following:
- Agriculture
- Distribution centers and warehouses
- Intralogistics in manufacturing
- Other environments such as logistics in retail and hospitals
- Mobile industrial robots also exist as prototypes or first models for domestic use. According to IFR, an estimated 69,000 units for logistic systems were installed in 2017 constituting of 63% of total professional service robots.
Industrial robots have often been used in complete automation systems in an increased variety of applications. At present, these robotic machines are applied as “next step” where automation is concerned. Their aim is to increase quality and productivity as well as reduce costs.