If you’re looking to help the environment, as well as save on the cost of gasoline, you’ve probably considered a hybrid vehicle before.
In premise, a hybrid vehicle is a great opportunity to make use of both, internal combustion and electric-powered motorization. But that’s not all.
In this article, we will cover everything you need to know, as well as how do hybrid cars work.
So keep reading to acquaint yourself with the knowledge pertinent to this topic.
Table of Contents
What Is A Hybrid Car & How Do Hybrid Cars Work?
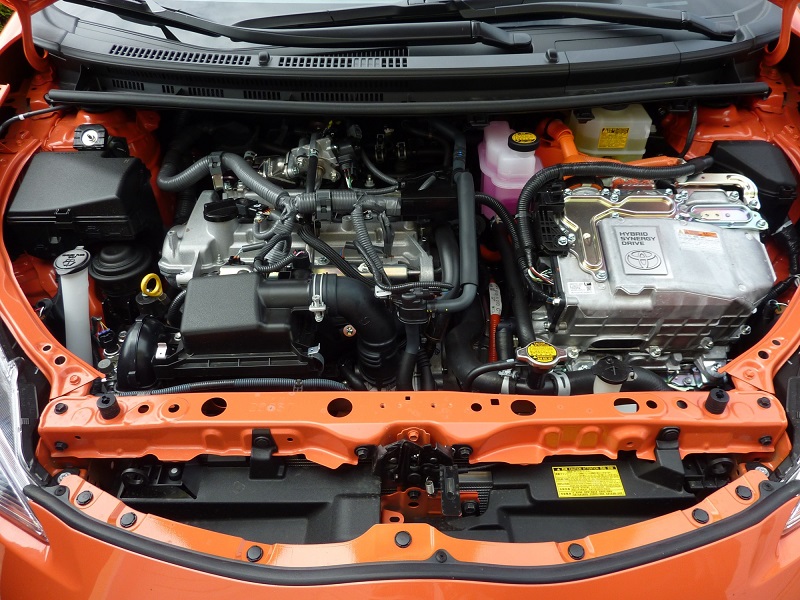
Hybrid in the context of the automobile industry refers to the ability of a vehicle to be powered by both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. The system works together, or separately to create drive force in the wheels.
The first mass-produced, modern hybrid car motor was inside of a Toyota Prius. The Prius has been updated many times since its debut in 1997. Better fuel economy is the primary concern for the faculty of hybridization.
But recently, auto manufacturers have noticed that even performance can be greatly improved. An electric motor gets the power from the battery pack that sits in the trunk behind the seats or the floor pan. This is done to lower the gravity center for better handling.
When certain driving conditions are best for an electric motor, such as being idle or driving below a certain speed, the combustion engine is turned off and does not consume gasoline.
When the battery is depleted or if lots of throttles are necessary, the combustion engine turns on and assists in both propelling the wheels forward, as well as recharging the battery. Are you still unsure of what are hybrid cars?
Well, let’s take a look at some of the most common hybrid vehicle types.
Parallel Hybrid
The most common of the hybrids is the parallel. This is a car in which both the electric motor and the combustion engine are present. The car is powered by the engine alone, the motor alone, or with both working together.
As mentioned earlier, the Toyota Prius is the greatest example of such a car. The battery in the car is charged by the engine, meaning there is no need to plug in. However, plugging in the charger can speed things up. The battery can also be charged with regenerative braking that stores kinetic energy and then transfers it to the battery.
The downside to this hybrid type of vehicle is that it can only drive for short distances, as well as in zero-emissions electric mode at significantly decreased speeds.
Plug-In Hybrid
A plug-in hybrid vehicle is similar to the prior type, as it also has both engine types. However, the difference is in the battery. It is larger.
This allows the vehicle to travel longer distances purely on electricity. Another important differentiating factor is that this type of vehicle prefers being plugged in for a charge.
Nonetheless, regenerative braking electric motor and combustion engine charging are still present. The owner of the car can charge their vehicle at home or one of the many charging points across the country.
A common example of this type of vehicle is the Mitsubishi Outlander. Plug-in hybrids are great for city commuters, not so much for long-haul drivers. This is a luxury that grid-connected individuals can make use of. In most cases, these vehicles cannot be driven entirely on internal-combustion.
Range-Extender Hybrid
While the internal combustion engine in plug-in and parallel hybrids can propel the wheels in motion, the range-extender hybrid cannot do that. The engine is not used for this purpose.
Instead, the engine is a very small petrol unit, and it is used entirely for charging the batteries when they lose their charge.
The car is entirely derived from an electric motor or several. Because the range-extender relies on the batter, these batteries are often much larger than the prior hybrid categories. As the range of pure-electric cars is increasing, range-extenders are slowly falling out of favor.
For instance, certain manufacturers like BMW stopped their production of such vehicles. And that’s about it for how do hybrid cars work. Let’s examine the pros and cons.
Pros & Cons Of Hybrid Cars
Hybrid cars make the most sense in cities and towns. Most parallel cars use the electric motor for low-speed driving. For instance, the vehicle cannot use the electric motor for speeds above 15 mph.
Furthermore, city driving involves lots of braking, therefore, the regenerative braking is evermore useful. It extends your driving distance, and the same applies to both range-extenders and plug-ins.
Both use the battery and electric motor to power most of the low-speed driving. Also, most plug-in hybrid vehicles are exempt from certain fines and charges. They also come with tax abatements, and benefits that help you save money. And in some cases make money.
Where hybrid cars don’t make much sense is in the long haul or motorway. That battery power is usually quickly drained, and it can be hard to find a charging station within proximity. Nonetheless, a double hybrid can always be driven via the internal combustion engine.
Hybrids Galore
Now that you know how do hybrid cars work, you are well on your way to determine if they are the right choice for you. In any case, whatever you choose to do, it will be the right thing to do.
Hybrid cars are great, but they are not necessary. If you’re interested in similar articles, feel free to check out the rest of our tech-related content on the sidebar.